Dissecting the Telehealth Niche
In this article, I’m going to be comprehensively dissecting the rapidly growing telehealth niche to uncover some of the most profitable opportunities emerging in this booming industry. Specifically, I’ll be showing you specialized research strategies that produce incredible insights – from high-intent keywords to extract, to hot affiliate programs aligned with telemedicine services, to overall market trends that signal areas primed for massive growth in the coming years.
Dissecting the telehealth Niche?
My goal is to showcase techniques that cut through the superficial level analysis and instead help drill down to find the most significant areas of potential within remote healthcare and virtual care. Whether you’re looking to start your own telemedicine practice or platform, invest in an exciting company pioneering new care models, develop niche content to gain authority fast, or evaluate joint venture partnerships, this framework will equip you with an unfair advantage. By seeing across the telehealth landscape with unique vantage points, you’ll gain backend access to exactly where outsized returns are waiting through untapped consumer demand. Let’s dive straight into dissecting the telehealth niche!
What is Telehealth?
Telehealth refers to the remote delivery of healthcare services through telecommunications technology. Also referred to as “telemedicine,” virtual care has expanded access and capabilities for patients and providers to connect. Rather than requiring in-office visits, telehealth allows patients to interface with doctors and specialists and support resources digitally from the comfort of their homes.
There are a variety of services that constitute telehealth. Core among them includes on-demand video consultations, often referred to as telemedicine appointments, which enable face-to-face diagnosis, treatment plans, and prescription orders to occur entirely virtually. Remote patient monitoring represents another avenue of telehealth, leveraging connected devices to track ongoing vitals like glucose levels so clinicians can assess changes without repeated visits. Overall, telehealth breaks the geographic barriers associated with traditional in-clinic care.
Rather than represent a niche branch of medicine, telehealth now interlinks with the broader healthcare continuum. Virtual solutions integrate with electronic health records, lab testing systems, prescription management, and medical billing infrastructure. As technology and regulation enable wider adoption, telehealth is positioned to transform everything from post-discharge care coordination to chronic condition coaching to triaging emergency scenarios. The capabilities grow more advanced annually.
The COVID-19 pandemic has expanded telehealth, with historic utilization booms changing patient and provider attitudes toward virtual interventions. However, technology and early market forces had already begun steadily building interest before mid 2020. Current forecasts suggest the impressive rise of telehealth is only just beginning as innovation accelerates.
1.tELEHEALTH, the statistics
Prior to the pandemic, analysts projected steady yet robust ORGANIC growth in the telehealth market. A research report from Markets and Markets forecasted compound annual growth of almost 22% from 2021 to 2026, estimating the global telehealth market size to expand from $79 billion to nearly $275 billion based on more significant adoption of remote patient monitoring systems and virtual healthcare delivery Additionally, a 2019 J.D Power survey found that telehealth utilization among U.S patients had increased from 9% to 15% year-over-year as virtual care integrated more into insurance networks and daily health routines (https://www.jdpower.com/business/press-releases/jd-power-2019-retail-healthcare-satisfaction-study). These data points reflected promising momentum.
However, the COVID-19 health crisis triggered an unprecedented national surge in telehealth and telemedicine utilization out of necessity and new care delivery priorities. A Doximity 2021 review of Medicare claims data found telemedicine claim lines soared 8,336% year-over-year in the U.S during the first COVID wave from March to October 2020 (https://www.doximity.com/news/telemedicine-utilization-report-2021). McKinsey research showed that up to $250 billion worth of current U.S healthcare spend has the potential to shift to virtual remoted delivery models post-pandemic, indicating a massive acceleration of market expansion (https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare-systems-and-services/our-insights/telehealth-a-quarter-trillion-dollar-post-covid-19-reality). While the pandemic catalyzed due to infection risks, analysts widely agree this demand boom reflects telehealth adoption has crossed the chasm to the mainstream rather than constituting a fading short-term phenomenon.
2. The Rise of Telemedicine Companies.
Pioneering Companies
The technology-fueled emergence of the telehealth industry has birthed an array of pioneering companies and platforms exclusively dedicated to delivering care through virtual and digital mediums, rather than just supplemental hospital system initiatives. Often referred to as telemedicine startups or virtual first care companies, these ventures represent a powerful trend of digitally native healthcare business models attuned fully to remote patient engagement from their infrastructure up.
Key telemedicine trailblazers include formally venture-funded unicorns like Teladoc Health, which has risen from being simply the main telehealth SaaS vendor to assuming an expansive care delivery role itself through aggressive M&A. Notable rivals include Amwell and Doctor on Demand, which similarly went public in response to COVID-era market appetite. Meanwhile, mental health platforms like TalkSpace have specialized solely around digital therapy appointments and found success. Large health systems are compelled to compete by acquiring more agile pure-play telemedicine firms rather than internal build capability.
While still an emerging field, the rise of dedicated telehealth pioneers has forced the hands of incumbents to follow suit in rapidly enabling virtual access channels. The result is an ascendant ecosystem of healthcare 2.0 companies fundamentally differentiating themselves through optimized user experiences, transparent pricing models, seamless coordination, and overall patient-centricity – while most crucially using remote care methods as their ultimate competitive edge. Their influence will only continue expanding care’s digital transformation.
major providers
The telehealth field features both digital health pure-play disruptors and with virtual offerings from established medical organizations. Leading pure-play providers include Teladoc Health, Doctors on Demand, and American Well (Amwell), which have amassed multi-million member bases through expansive telemedicine offerings focused on in-network virtual primary, chronic and specialist care. Usage of their platforms boomed during peak COVID times, with Teladoc reportedly conducting over 10 million virtual visits by the end of 2020.
Adoption Metrics
Adoption metrics specific to the US market indicate telehealth utilization peaked at nearly 38% of consumers using services in 2020, up from just 11% and stagnating metrics pre-pandemic. While this has leveled closer to 21% into 2022, it still reflects drastic permeation into consumer healthcare habits post-COVID versus historically. Notably, behavioral health reflects the highest specialty telemedicine adoption at over 75%. Behavioral health is another term for mental health. Overall, behavioral health means considering a patient holistically across mental, emotional, social, and decision-making capacities – not just the absence of mental illness. It ties closely to notions of resilience and human thriving. The applied field aims to help people achieve fulfilling lives despite stressors.
Software, hardware, and devices enabling virtual visits
Software
Fundamental to delivering a quality telehealth consultation is robust software powering seamless video conferencing, compliance with healthcare data protections, integration with medical records, and tools to collect patient health inputs. Popular platforms include Doxy.me, VSee, thera-Link, and Amazon Chime specifically for telemedicine. Features like screen sharing, notes, and file uploads make remote diagnosis possible.
Hardware
From a technology standpoint, hardware elements like internet bandwidth, computer/device webcam quality, microphone functionality, and WiFi connection strength also significantly factor into virtual visit reliability. Optimized in-clinic telehealth carts typically use dual screens, specialty cameras, and Bluetooth medical device pairing for remote monitoring and diagnostic peripherals.
Data Collection Devices
Expanding telehealth capabilities also involves supplemental measurement and data collection devices used in tandem with consultations. Connected blood pressure cuffs, scales, thermometers, pulse oximeters, and glucose monitors allow vital tracking between visits. Paired mobile apps build health dashboards. Several FDA-approved mobile devices like AliveCor’s KardiaMobile EKG transmitter enhance clinicians’ diagnostic accuracy without in-person presentment. This is rounded off with the availability of home test kits.
While software lays communication/security groundwork and hardware provides connectivity, emerging supplemental devices create opportunities to gather, share, and evaluate patient health data in ways previously requiring physical appointments. The interplay of these technical workflow components underpin telemedicine delivery modalities.
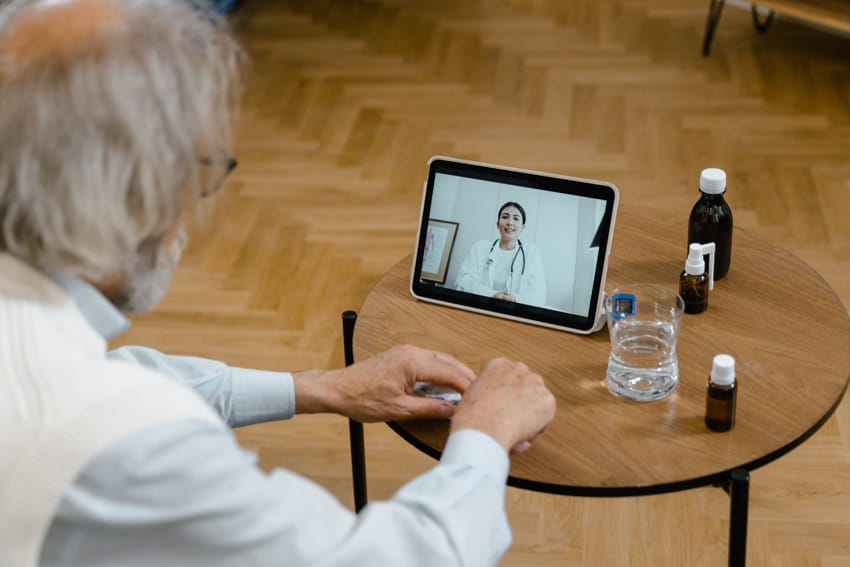

key steps for developing a telehealth business,
1 For clinicians and healthcare entrepreneurs interested in offering telemedicine services, the first step entails getting fully credentialed to practice medicine remotely in compliance with state licensure policies, DEA registrations, and liability coverage requirements, which vary across geographic regions. Selecting an established telehealth provider partner can streamline this process. Certification courses also exist to learn clinical best practices.
2. Technology Side. On the technology side, configuring HIPAA-compliant platforms for securely hosting virtual visits and protecting sensitive patient information is paramount. Turnkey software as a service options eliminate the need for custom development. However, mapping out integrations with pharmacy systems, medical billing tools and health records databases is beneficial for seamless coordination and care continuity. Tablets and diagnostic peripherals also help collect and share pertinent health data.
3. Independant Practicioner’s.When preparing to launch, an independent practitioner should outline the nature of remote services specializing in areas like chronic care management for seniors, pediatric health, nutrition advice, or counseling. Business model decisions around fee structures for self-pay vs insured clients also take shape. Meanwhile, medical directors at larger telemedicine companies oversee provider hiring strategies and clinical standardization.
4. Bookings. As telehealth offerings open for booking, processes solidify around appointment reminders, patient pre-screening procedures, visit documentation protocols and follow-up sequence. Marketing to acquire patients remains ongoing through search optimization, community partnerships and referral programs. Over time, ancillary services get added to meet demand.The key is identifying frequent needs cropping up for telehealth patient bases and creating offerings to serve those needs synergistically with core virtual visit services, making engagement frictionless.
Conclusion to the Telehealth niche
The telehealth sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological advancements and a global shift towards digital healthcare solutions. This expansion presents significant opportunities for entrepreneurs and investors. However, success in this niche requires a deep understanding of regulatory landscapes, technological infrastructure, and patient engagement strategies. By staying informed about industry trends and prioritizing user-centric services, stakeholders can effectively navigate the complexities of the telehealth market and capitalize on its potential.








The remote delivery of healthcare services is an interesting offshoot in the medical field. Patients and providers can now connect online which saves much time and expense. Thanks for sharing all the pertinent details.
The remote delivery of healthcare services, or *telehealth*, has indeed revolutionized the way medical care is provided and received. The ability for patients and providers to connect virtually has broken down geographical barriers, making healthcare accessible even to those in remote or underserved areas. For individuals living far from medical facilities—or those with mobility challenges—telehealth eliminates the need for long commutes, reducing not only travel time but also associated costs. It’s a shift that has particularly gained momentum during and after the COVID-19 pandemic when in-person visits became impractical or even risky.
Another major advantage of telehealth is the ability to facilitate **continuous care** and **follow-ups**. Patients managing chronic illnesses, mental health concerns, or post-surgical recovery can consult with healthcare providers regularly, ensuring consistent monitoring without the hassle of frequent clinic visits. Additionally, telehealth reduces wait times in traditional medical settings and allows doctors to optimize their schedules, offering flexibility for both parties. Technologies such as remote diagnostics, wearable health trackers, and secure video platforms further enhance this interaction by providing real-time health data.
However, despite its clear benefits, telehealth isn’t without its challenges. Not everyone has reliable internet access or the technological know-how to utilize these services effectively. There are also concerns regarding the **quality of care** for cases that might require physical examinations. Additionally, maintaining data security and patient confidentiality in a digital environment is an ongoing issue that healthcare providers must tackle carefully.
Telehealth represents an exciting shift towards a more accessible, efficient healthcare system, but it also raises questions about **how to balance virtual care with the need for traditional, in-person consultations**. Do you think telehealth can fully replace physical visits, or will we always need a hybrid model to achieve the best outcomes?